对于DB中更新不频繁的数据使用缓存可以大大提高查询效率。MyBatis 作为一款非常流行的持久层框架,自然是提供了缓存支持的。MyBatis支持一级缓存和二级缓存。在没有配置的默认情况下,它只开启一级缓存。
一级缓存
一级缓存只对同一个SqlSession有效,在SQL和参数完全一样的情况下,我们使用同一个SqlSession第一次查询后,MyBatis会将其放入缓存中,以后再查询的时候,如果缓存没有被刷新过,并且没有超时的情况下, SqlSession都只会取出当前缓存的数据,而不会再次发送SQL到数据库。
下面看一个例子:
1 | |
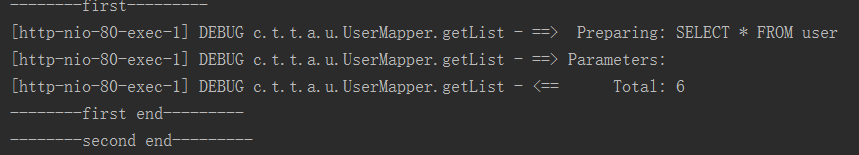
第一次调用getList()方法时从数据库查询, 第二次调用会直接从缓存中取出数据,日志如下图所示。
关闭一级缓存
如果不想开启一级缓存,该如何关闭它呢?先看看MyBatis配置中与一级缓存有关的配置项
| 设置 | 描述 | 可选值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| localCacheScope | 设置缓存范围。设置为SESSION时会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询,为 STATEMENT时本地会话仅用在语句执行上,相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据 | SESSION | STATEMENT | SESSION |
要关闭一级缓存,只需要在MyBatis的配置文件中将localCacheScope设置为STATEMENT就可以了。
1 | |
注意,只有在开启事务的情况下,一级缓存才起作用。
二级缓存
一级缓存只在同一个SqlSession中有效,二级缓存的作用范围更大,多个sqlSession可以共享一个Mapper的二级缓存区域。MyBatis二级缓存默认是关闭的,需要在配置文件中配置开启它,并且要求返回的POJO必须是可序列化的,也就是要实现Serializable接口。
开启二级缓存
在核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml中加入
1 | |
在映射xml文件中配置cache,就可以开启二级缓存了。
1 | |
下面来测试一下二级缓存 映射器配置:
1 | |
Controller代码:
1 | |
分别访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/getAll 和 http://127.0.0.1:8080/getAll2, 第一次从数据库查询,第二次从Cache获取。说明二级缓存生效了。
1 | |
Cache属性
1 | |
上面的配置创建了一个 LRU 缓存, 并每隔 60 秒刷新, 最多可以存储 1024 个对象, 并且这些对象是只读的。
- eviction : 代表缓存回收策略, 默认的是 LRU 。目前MyBatis提供以下策略:
- LRU:最近最少使用的,移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO:先进先出,按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT:软引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK:弱引用,更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
- flushInterval:刷新间隔时间,单位为毫秒。如果不设置, 那么当SQL被执行的时候才会去刷新缓存。
- size:引用数目, 一个正整数,代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,不宜设置过大(内存溢出)。默认值是 1024。
- readOnly:只读,意味着这些对象不能被修改只能被读取,好处是可以快速读取缓存,缺点是没法修改。默认是 false。
禁用二级缓存
在statement中设置 useCache=false 可以禁用当前select语句的二级缓存,即每次select都去DB查询,默认情况是true。 针对每次查询都需要最新数据的SQL,要设置成useCache=false,禁用二级缓存。
1 | |
flush缓存
在同一个mapper中,执行完 insert、update、delete 操作后需要刷新缓存,否则 select 时会出现脏数据。 元素中有一个 flushCache 属性,若将其设置为true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空。
下面是insert的配置例子:
1 | |
select语句
| 属性 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空 | false |
| useCache | 将其设置为 true,将会导致本条语句的结果被二级缓存 | 对 select 元素为 true |
insert、update、delete语句
| 属性 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| flushCache | 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空 | true |